

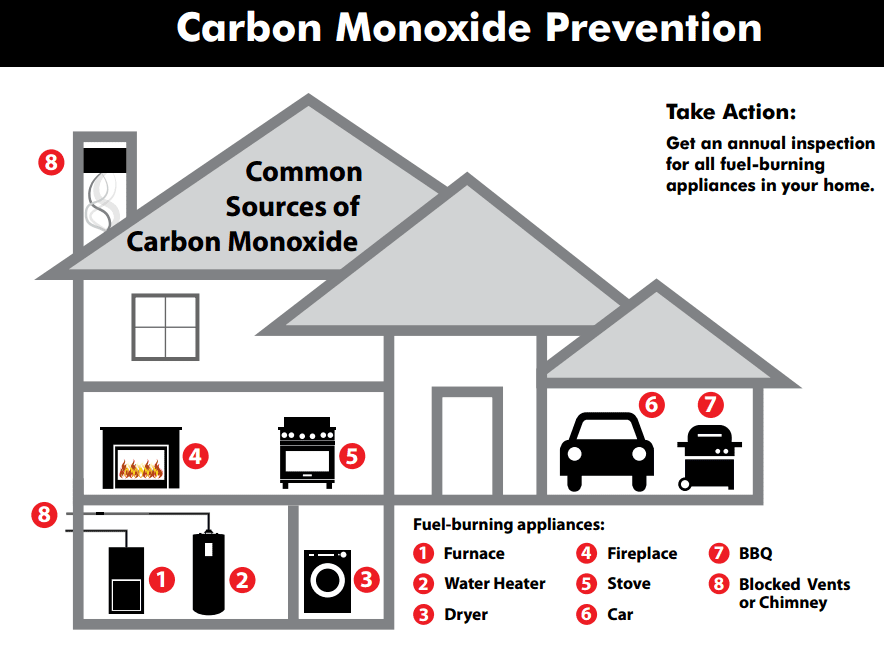
Carbon monoxide (CO) is an odorless and colorless gas that can cause severe illness or death. It is produced any time fossil fuels are burned. During a power outage, the use of gas generators or outdoor grills in carports or too close to the home can trap CO in the home and cause CO poisoning. Other possible sources of CO include small gasoline engines, stoves, lanterns, burning charcoal and wood, gas ranges and heating systems.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, at least 430 people die from accidental carbon monoxide poisoning in the United States every year. And each year, around 50,000 people go to the emergency department from CO poisoning.
Here are ways to be safe from carbon monoxide poisoning.
- Do not use items that produce carbon monoxide inside your home or garage or outside an open window.
- Never use gas ovens to heat your home, even for a short time.
- If you use a fireplace or wood stove, make sure that chimneys and flues are in good condition and are not blocked.
- Never idle a car in a garage, even when the garage door is open.
- Make sure carbon monoxide alarms are installed on every level of your home and outside every sleeping area. Test your CO alarms along with your smoke alarms monthly and change the batteries at least once a year.
If your home CO alarm beeps continuously without stopping, it could indicate that carbon monoxide is present. If your CO alarm is sounding continuously and you have signs of CO poisoning such as dizziness, headache, vomiting or flu like symptoms, find fresh air and call 9-1-1 immediately.
Contact the Seattle Fire Department to see if you qualify for a free installed combination smoke/carbon monoxide alarm. Learn more here.
Learn more: